Example For Transport Protein
16052020 Active transport is most commonly accomplished by a transport protein that undergoes a change in shape when it binds with the cells fuel a molecule called adenosine triphosphate ATP. The hemoglobin is example for transport protein read more.
Active Transport Ck 12 Foundation
Myoglobin another transport protein then takes oxygen from the hemoglobin and stores it until it is needed in muscle tissue.

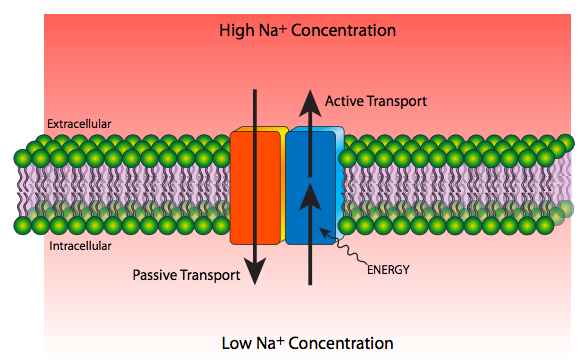
Example for transport protein. A special kind of protein called apolipoprotein is embedded in the outer shell both stabilising the complex and giving it a functional identity that determines its role. Channels work as particular pathways for the fast pervasion of particles moving down an electrochemical slope. In the example above we discussed how the cell uses ATP to maintain the sodium and potassium gradients between the inside and outside of the cell.
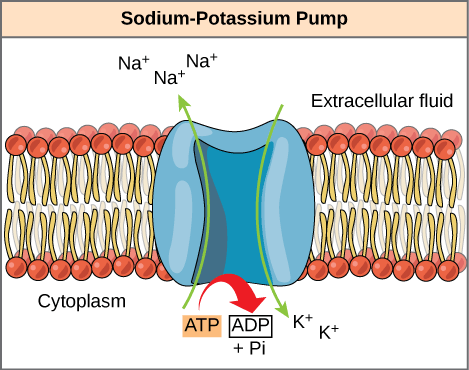
There are different types of channel proteins for different molecules including ones for sodium. The sodium-potassium pump transports sodium and potassium ions across the cell membrane against their concentration gradient. For example the sodium gated channels of a nerve cell are stimulated by a.
11052018 Hemoglobin is an example of an oxygen-transport protein and is a part of these oxygen delivery systems. A single human hemoglobin molecule consists of four polypeptide chains. Each of these chains contains a tightly bound prosthetic group called heme.
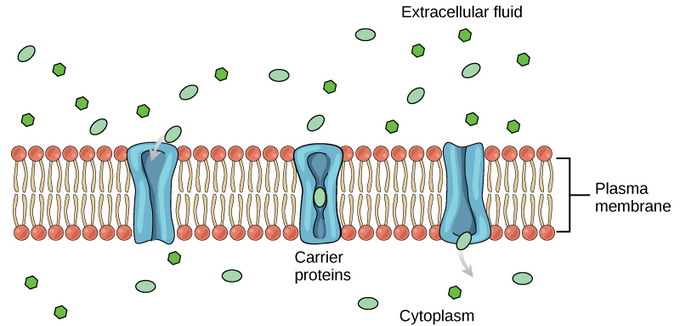
In the example above we discussed how the cell uses ATP to maintain the sodium and potassium. Examples include plasma lipoprotein particles HDL LDL IDL VLDL and. Channel proteins gated channel proteins and carrier proteins are three types of transport proteins that are involved in facilitated diffusion.
For example one type of active transport channel in the cell membrane will bind to the molecule it is supposed to transport such as a sodium ion. The transporter protein are specific however some can transport multiple compounds. For example a calcium channel can only be used to transport calcium in and out of the cell.
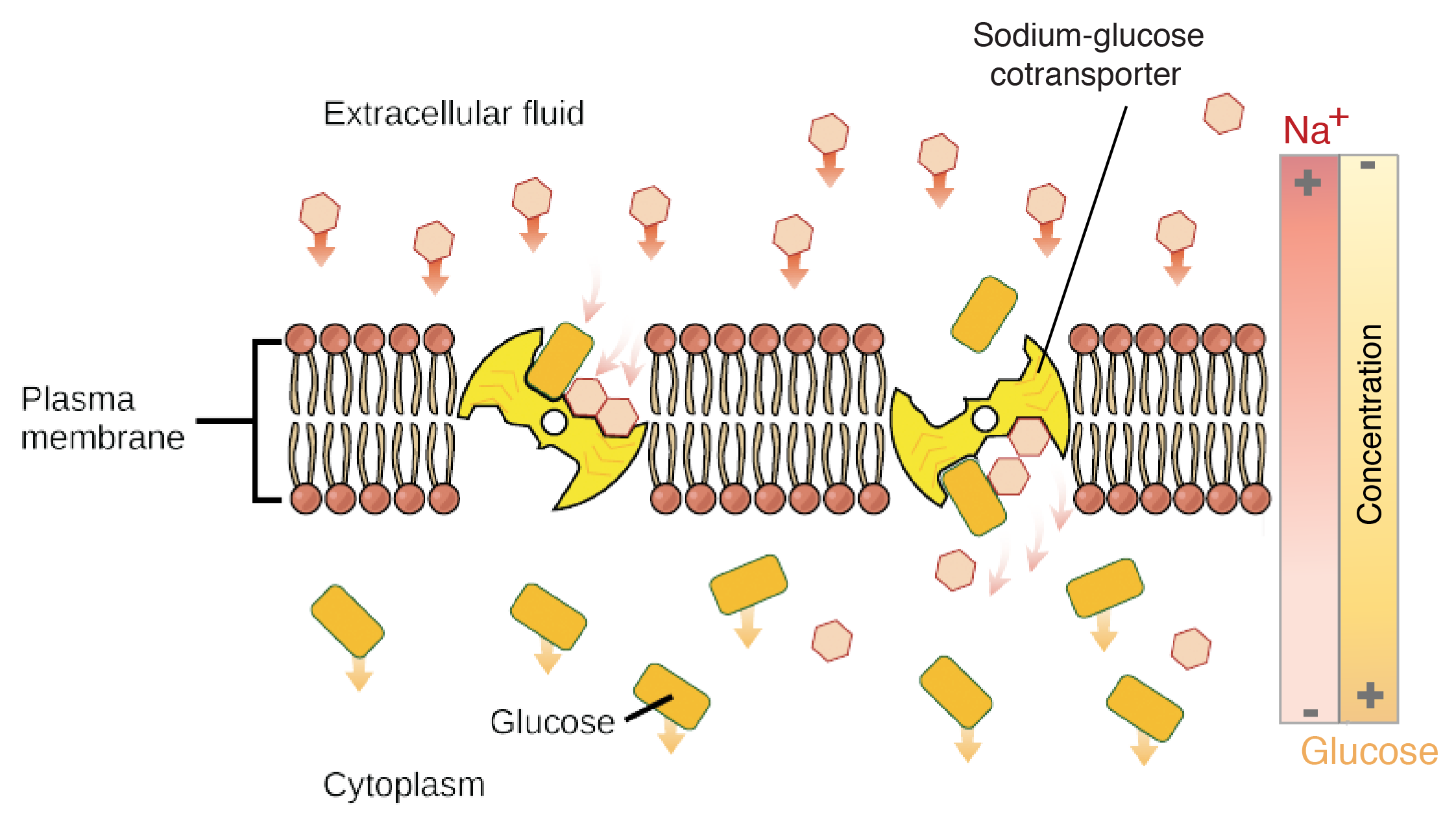
The glucose-sodium cotransport protein is a good example of a protein that uses secondary active transport by indirectly using ATP. 02082017 The transporter protein is known as Permease or Porter or carrier protein. 03012021 On the other hand the classic example of an active transport protein the Na K ATPase also known as the Na K antiport utilizes the energy from ATP hydrolysis to power the conformational changes needed to move both Na and K ions against the gradient.
Transport proteins can go about as channels pumps or transporters. Phagocytosis of bacteria by Macrophages. In a third type of active transport large items or large amounts of extracellular fluid may be taken into a cell through the process of endocytosis.
Sodium-glucose transporter that cotransport glucose and sodium in the small intestine. Carrier proteins are integral membrane proteins. Saccharomyces cerevisiae has been used as a model system to probe the underlying mechanisms of nuclear transport and how they regulate various physiological processes.
Movement of Ca 2 ions out of cardiac muscle cells. Many enzymes transporters structural proteins antigens adhesins and toxins are lipoproteins. Channels are layer proteins that effectively transport particles against their electrochemical slope to the detriment of a cells wellspring of energy for example ATP.
Carrier proteins are proteins involved in the movement of ions small molecules or macromolecules such as another protein across a biological membrane. These transporters play a significant role in drug absorption and distribution to organic systems particularly if the organs are protected by blood-organ barriers such as the blood-brain barrier or the maternal-fetal barrier. Active transport requires transporter protein and continuous supply of cellular energy for the transport.
There are several different kinds of transport proteins. 14112016 The glucose-sodium cotransport protein is a good example of a protein that uses secondary active transport by indirectly using ATP. Transportation of amino acids across the intestinal lining in the human gut.
05032021 A transport protein completely spans the membrane and allows certain molecules or ions to diffuse across the membrane. Glucose transport protein or GLUTs that transport glucose and other hexose sugars. Regulated protein transport between the cytoplasm and the nucleoplasm occurs through nuclear pore complexes and is critical to the function of numerous biological pathways.
Drug transporters are membrane proteins present in various tissues such as the lymphocytes intestine liver kidney testis placenta and central nervous system. That is they exist within and span the membrane across which they transport substances. 20072020 Some of the best examples of active transport include.
At first solute molecule binds with the transporter protein and changes the 3D structure of the transporter protein and this change in shape allows the solute to carried across the membrane.
Active Transport Primary Secondary Overview Article Khan Academy
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn And9gcstcwuyczfbfpnpprdbjhr5brevoeyug7wb75jclnv4mrcx6fxa Usqp Cau
Cell Transport And Homeostasis Ck 12 Foundation
Transport Across The Cell Membrane Boundless Microbiology

Transport Across Membranes Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
4 3 Membrane Transport Proteins Biology Libretexts

Active And Passive Transport Let S Learn Science
Pumps Active Transport Definition Types Expii

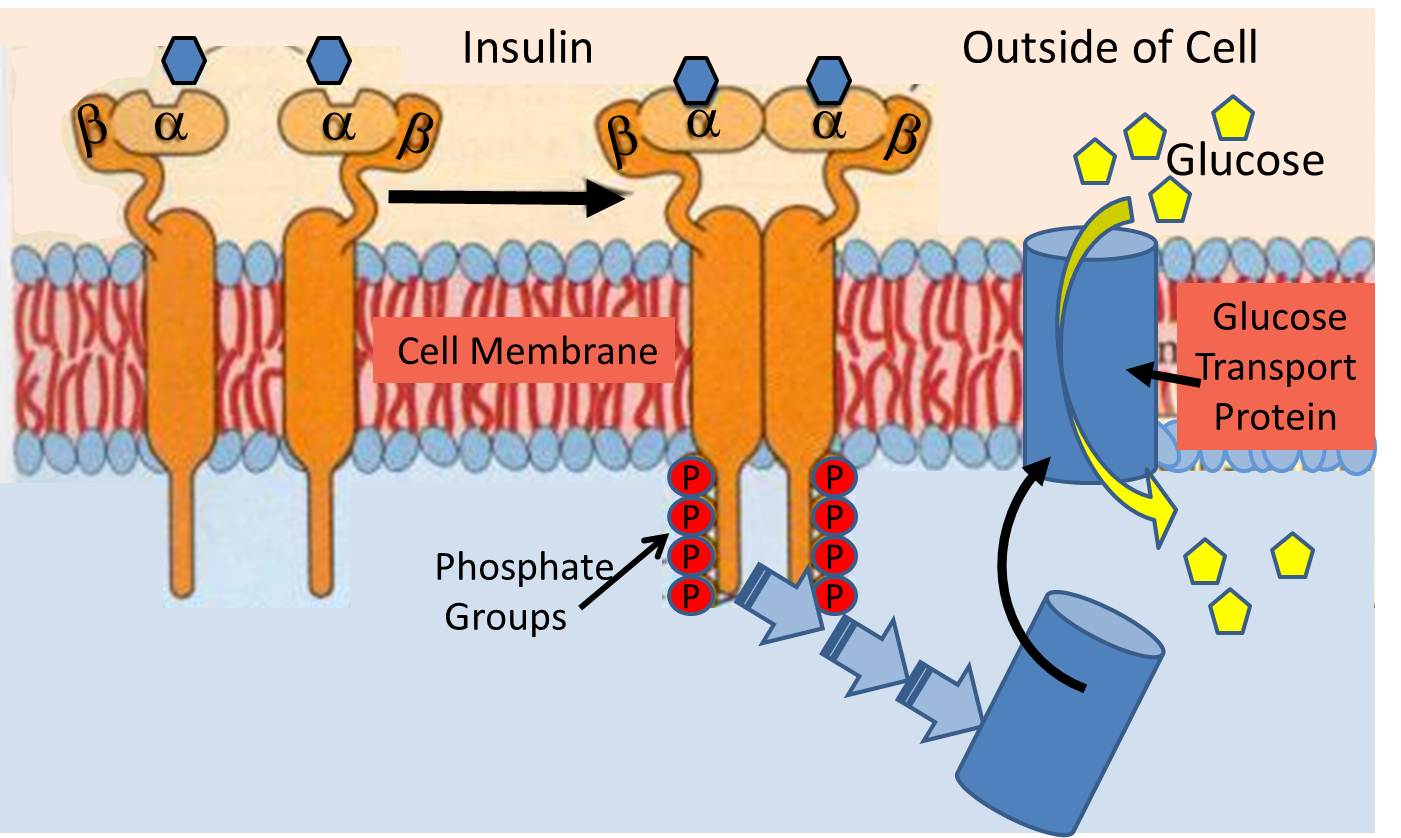
Post a Comment for "Example For Transport Protein"